About Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What is squamous cell carcinoma?
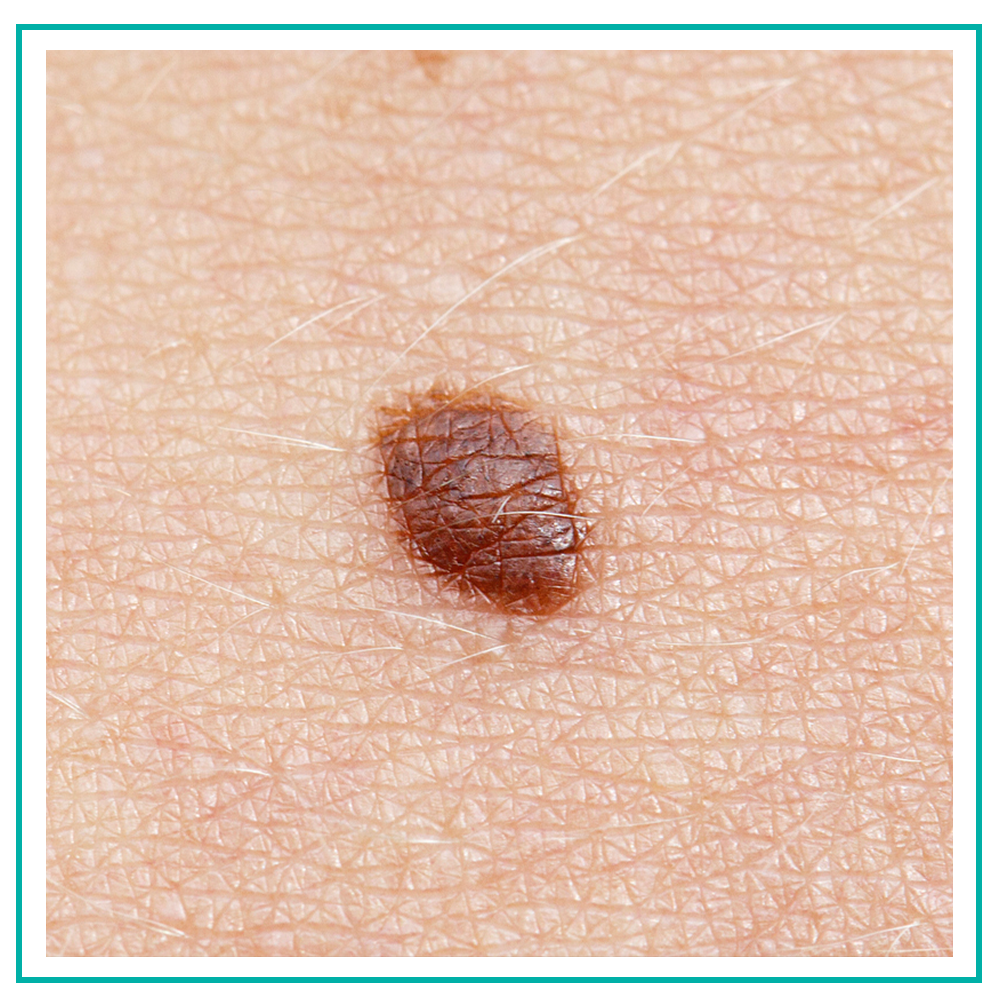
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer. It occurs most frequently on sun-exposed regions of the body. It can look like a scaly red patch, a wart-like growth, a pink bump that might be confused for a pimple or bug bite, or sometimes as a brown spot. Squamous cell carcinomas can bleed, form an open sore, or become tender with time, but they are not always symptomatic. They are usually not life-threatening but can spread to other areas of the body (metastasize) if left untreated.
Are certain people more at risk?
People with fair skin, light hair and blue, green or grey eyes are more at risk, but squamous cell carcinomas an occur in anyone. People who are immunosuppressed, such as organ transplant recipients, are also at increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
How can we protect ourselves?
Chronic overexposure to sunlight is the leading cause of squamous cell carcinoma.